Hair Transplant:
Hair Transplant:
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure performed to treat hair loss or baldness by relocating hair follicles from one part of the body (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to the bald or thinning areas. It’s primarily used to address male-pattern baldness, but it can also help women with hair thinning or other types of hair loss.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
Also known as strip harvesting, this technique involves removing a strip of skin from the donor area (usually the back of the scalp) where hair follicles are abundant. The strip is dissected into individual grafts containing hair follicles, which are then transplanted into the balding or thinning areas.
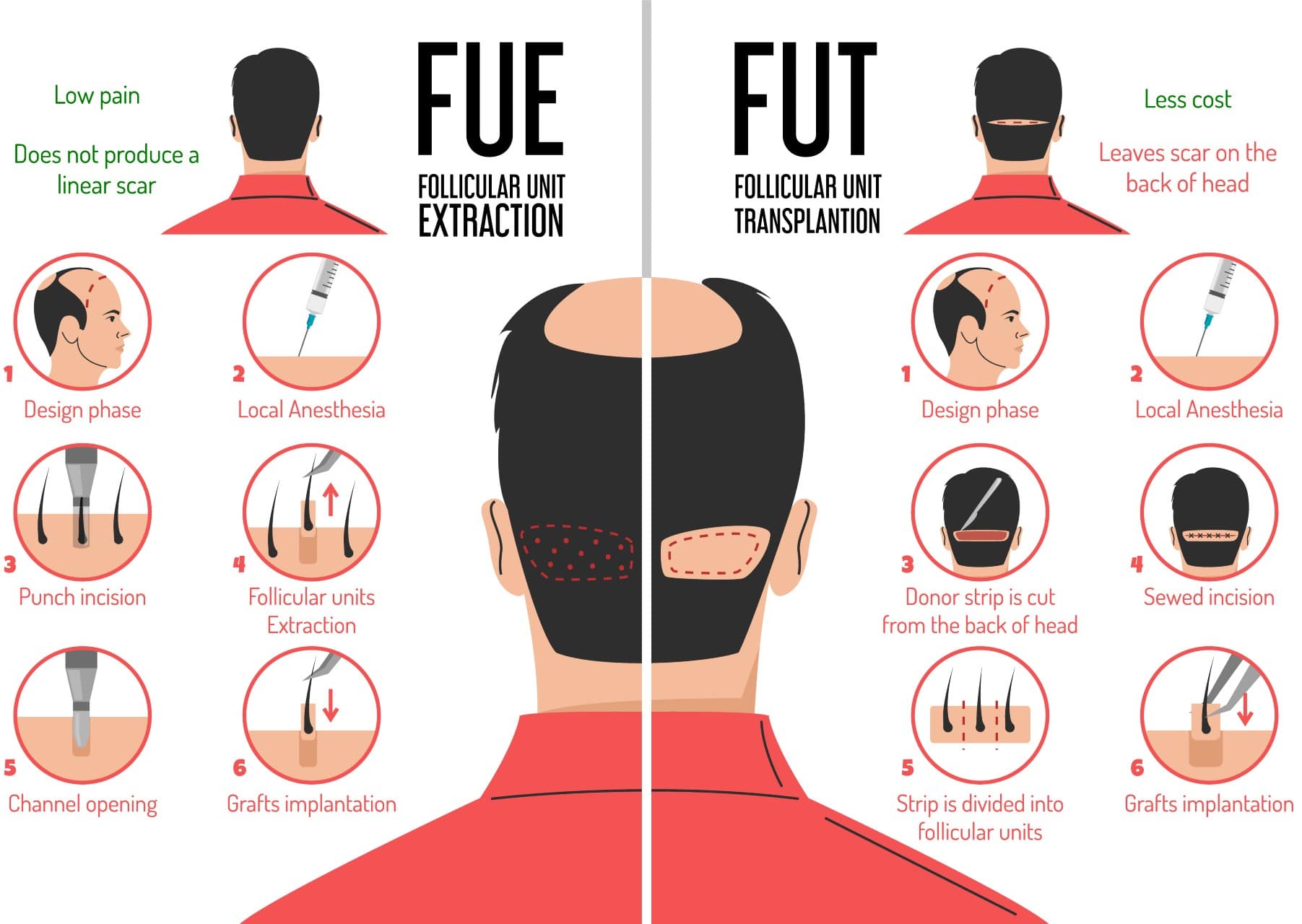
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
In this method, individual hair follicles are extracted directly from the donor area using tiny punches or instruments. The follicles are then implanted into the recipient area, where hair growth is desired. FUE doesn’t involve the removal of a strip of skin and leaves tiny scars that are less noticeable than those from FUT.
The transplantation process involves careful planning and placement of the hair grafts to achieve a natural-looking hairline and density. The success of the procedure depends on factors like the quality and quantity of donor hair, the surgeon’s expertise, and the patient’s expectations.
After the surgery, there will be a healing period during which the transplanted hair falls out. New hair growth typically begins within a few months, and it may take several months for the full results to become noticeable. Post-operative care is essential to ensure proper healing and optimal results.
Hair transplant surgery is generally considered safe, but like any surgical procedure, it carries potential risks such as infection, bleeding, scarring, and, in some cases, an unnatural appearance if not performed correctly.

