Joint Replacement Surgery:
Joint Replacement Surgery:
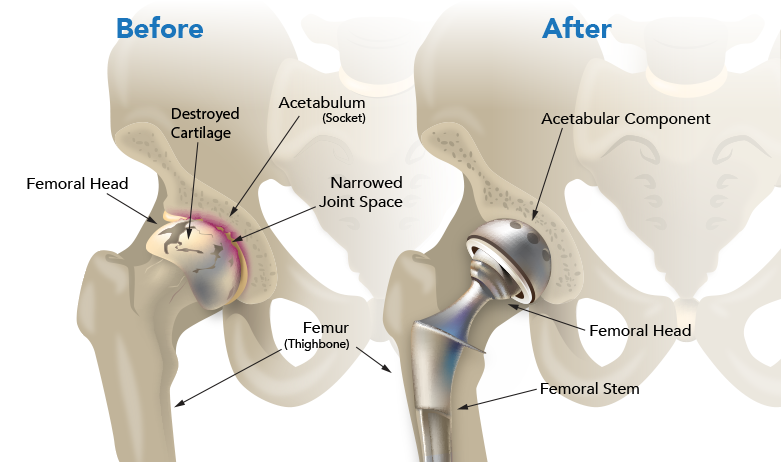
Here are some key aspects of joint replacement surgery:
Reasons for Surgery: Joint replacement is typically considered for joints that have severe damage due to conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, post-traumatic arthritis, avascular necrosis, or other joint diseases that cause pain, stiffness, and limit mobility.
Types of Joint Replacements: The most common joint replacements include hip replacements, knee replacements, and shoulder replacements. Other joints, such as the ankle, elbow, or wrist, may also undergo replacement surgery but are less common.
Surgical Procedure: During the surgery:
- The damaged or worn-out parts of the joint are removed.
- The prosthesis made of metal, plastic, or ceramic components is then implanted to replace the damaged joint.
- The surgery may involve replacing the entire joint (total joint replacement) or only the damaged parts (partial joint replacement).
Recovery and Rehabilitation: After surgery, patients undergo a period of recovery that includes pain management, physical therapy, and rehabilitation exercises to regain strength, mobility, and function. Most patients can resume normal activities gradually, following the guidance of their healthcare team.
Risks and Complications: While joint replacement surgery is generally safe and successful, it carries potential risks, including infection, blood clots, implant loosening, implant wear, nerve damage, or joint stiffness. These risks are typically minimized by careful pre-operative evaluation, surgical technique, and post-operative care.
Long-Term Outcomes: Joint replacement surgery can provide significant pain relief, improved joint function, and enhanced quality of life for many individuals. Proper care, regular follow-ups, and adhering to medical advice are essential for the long-term success of the joint replacement.

